Bulging Disc Treatment: What You Should Know
Anyone who has ever experienced back pain knows how much it can interfere with life. Even mild back pain can cause you to miss out on your favorite activities, and more severe pain, like that caused by a bulging disc, can make everyday life difficult. If you’ve been diagnosed with a bulging disc or suspect you have one, the path to a pain-free life is with proper treatment. Here’s what you should know about bulging disc treatment.
What is a Bulging Disc?
A bulging disc occurs when one of the spinal discs extends beyond its normal boundary without rupturing through its outer layer. These discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae in your spine, can bulge out due to wear and tear, injury, or breaking down over time.
Symptoms of a Bulging Disc
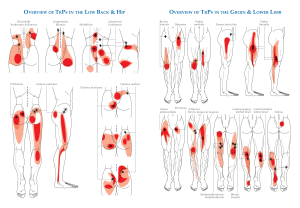
A bulging disc can press against nearby nerves and tissues, leading to various symptoms such as:
- Localized pain at the site of the bulging disc
- Radiating pain that travels from the spine to other areas, such as the arms or legs
- Sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities
- Muscle weakness in the affected area.
Identifying the Causes and Risk Factors of Bulging Discs
Several factors can contribute to the development of a bulging disc:
- Aging. Natural wear and tear over time can weaken the discs
- Injury. Trauma to the spine can cause discs to bulge
- . A condition where the discs break down and lose their cushioning ability
- Poor posture. Slouching in chairs or hunching over phones and computers can strain your vertebrae excessively.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Lack of exercise can weaken the muscles supporting the spine.
Diagnosing a Bulging Disc
To diagnose a bulging disc, your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination and may recommend imaging tests such as:
- X-Ray for ruling out other causes of pain and discomfort
- CT Scan to visualize the spine and detect abnormalities
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for detailed images of the spine and discs
During the exam, your doctor will see how much pain you’re in, test your muscle reflexes, check your sensation, and measure your muscle strength. This helps them understand the extent of your condition.
Treatment Options for Bulging Discs
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense in managing bulging discs. These treatments aim to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. Common non-surgical treatments include:
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
- Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Engaging in physical therapy and exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility
- Using oral steroids or steroid injections to reduce inflammation
When Surgery is Needed
Surgical intervention may be considered if conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if symptoms are severe. Types of surgical procedures for bulging discs include:
- . Removal of the bulging disc material pressing on a nerve
- Foraminotomy. Surgery to widen the opening where nerve roots exit the spine
- . Joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine and reduce pain
- Artificial . Replacing the damaged disc with an artificial one
Preventing Bulging Discs
The following measures can help reduce the risk of developing a bulging disc:
- Ensure proper posture and alignment of the spine during daily activities.
- Exercise regularly and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
- Reduce stress on the spine by avoiding excess weight.
- Avoid smoking because it can contribute to disc degeneration.
- Use proper body mechanics when lifting heavy objects.
When to See a Neurosurgeon or Physiatrist
If you’re experiencing back pain or think you might have a bulging disc, it’s a good idea to talk to a specialist who can create a treatment plan just for you. Our neurosurgeons and physiatrists are here to help, offering both conservative and surgical options to ensure you get the best care possible.
Don’t continue to live with pain and get started with bulging disc treatment – today!